This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
LAB9: Particle Systems (Optional)
In this lab we will scratch the surface of using the Bullet physics blibrary with Ogre. This lab is intirely optional but can replace another previously unfinished lab, and counts toward participation.
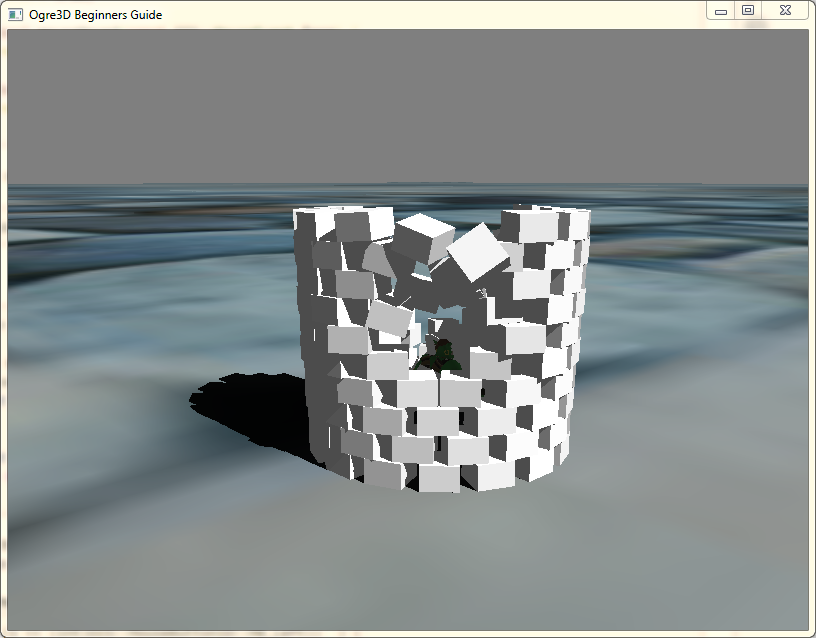
Unfortunately I was unable to give me the proper amount of time to make this lab interesting enough, but the classic brick wall vs cannon will have to do :)

Discussion
Discussion thread for this lab is on Piazza
Preperation
You can use your own project or start fresh with the base application code
Lab
- Setup Project.
- Downlaod Bullet
- Build Bullet
- Run <bullet root>\build\vs2010.bat to generate the VS 2010 project files.
- Open the <bullet root>\build\vs2010\0BulletSolution.sln With you VS of choice.
- Make sure you compile using the v100 version of the visual studio compiler
Note: that you can select properties for one project, then multi select the projects you want to change the properties for to change the value in multiple projects at the same time. - Change the C/C++→Code Generation→Runtime Library to Multi Threaded DLL (/MDd (Debug) and /MD (Release))
- Build the solution for debug and release.
- Add
<Bullet Root>\lib;toLinker→General→Additional Library Directories(Debug and Release) - Add
<Bullet Root>\src;toC++→General→Additional Include Directories(Debug and Release) - Add
BulletCollision_vs2010_debug.lib;BulletDynamics_vs2010_debug.lib;LinearMath_vs2010_debug.libto theLinker→Input→Additional Dependencies(Debug) - Add
BulletCollision_vs2010.lib;BulletDynamics_vs2010.lib;LinearMath_vs2010.libto theLinker→Input→Additional Dependencies(Release) - Create class Physics.
// Header! #ifndef PHYSICS_H #define PHYSICS_H #include "btBulletCollisionCommon.h" #include "btBulletDynamicsCommon.h" #include <vector> #include <map> class Physics{ btDefaultCollisionConfiguration* collisionConfiguration; btCollisionDispatcher* dispatcher; btBroadphaseInterface* overlappingPairCache; btSequentialImpulseConstraintSolver* solver; btDiscreteDynamicsWorld* dynamicsWorld; std::vector<btCollisionShape *> collisionShapes; std::map<std::string, btRigidBody *> physicsAccessors; public: Physics(); virtual ~Physics(); btDiscreteDynamicsWorld* getDynamicsWorld(); }; #endif //PHYSICS_H // Implementation! #include "Physics.h" Physics::~Physics() { delete dynamicsWorld; delete solver; delete overlappingPairCache; delete dispatcher; delete collisionConfiguration; } void Physics::initObjects() { collisionConfiguration = new btDefaultCollisionConfiguration(); dispatcher = new btCollisionDispatcher(collisionConfiguration); overlappingPairCache = new btDbvtBroadphase(); solver = new btSequentialImpulseConstraintSolver(); dynamicsWorld = new btDiscreteDynamicsWorld(dispatcher, overlappingPairCache, solver, collisionConfiguration); } btDiscreteDynamicsWorld* Physics::getDynamicsWorld() { return dynamicsWorld; }
- Create a pointer to physics in your Application, and initialize it in the startup function.
- Before we start there are some basic changes that have to made to the environment, in order to make the physics look more realist, we must make sure that our environmet is in a logical scale. If you have the handout code, Sinbad will be around 9.5 units high, Bullet library uses 1 unit as equal to 1 meter.
- You can check out Sinbad's actualt height by doing
_SinbadNode→getBoundingBox().getSize(), this function will return the bounding box the the sceneNode, which is an axis aligned box that encompasses the entities of the SceneNode and is defined by the vertex extremas + an additional 2% scale. - Now scale the sinbad node down by 0.2
_SinbadNode→scale(Ogre::Vector3(0.2f,0.2f,0.2f)); - Change the nearClippingPlaneDistance of the camera to 0.5
- In the frameListener class, change the movement speed of the camera to something around 10-20.
- Now to create Rigid Bodies we must first let bullet know what form of rigid body we want, and we must also tell bullet the size, position and orientation of our RigidBody.
- Add this function to your Physics class.
btRigidBody* AddDynamicCubeRigidBoidy(Ogre::SceneNode* node, Ogre::Entity* ent, btScalar mass) btRigidBody* Physics::AddDynamicCubeRigidBoidy(Ogre::SceneNode* node, Ogre::Entity* ent, btScalar mass) { Ogre::Vector3 aabbSize = ent->getBoundingBox().getSize() / 1.02; btScalar x = 0.5 * node->getScale().x * aabbSize.x; btScalar y = 0.5 * node->getScale().y * aabbSize.y; btScalar z = 0.5 * node->getScale().z * aabbSize.z; btCollisionShape* colShape = new btBoxShape(btVector3(x, y, z)); /// Create Dynamic Objects btTransform startTransform; startTransform.setIdentity(); //rigidbody is dynamic if and only if mass is non zero, otherwise static bool isDynamic = (mass != 0.f); btVector3 localInertia(0, 0, 0); if (isDynamic) colShape->calculateLocalInertia(mass, localInertia); startTransform.setOrigin(btVector3(node->getPosition().x, node->getPosition().y, node->getPosition().z)); btQuaternion initRotation(node->getOrientation().x, node->getOrientation().y, node->getOrientation().z, node->getOrientation().w); startTransform.setRotation(initRotation); OgreMotionState* motionState = new OgreMotionState(startTransform, node); btRigidBody::btRigidBodyConstructionInfo rbInfo(mass, motionState, colShape, localInertia); btRigidBody* body = new btRigidBody(rbInfo); dynamicsWorld->addRigidBody(body); return body; }
- As you might have noticed, that function uses a class called OgreMotionState, this is a class that we must implement in order for Bullet to automatically transoform our SceneNode according to the movement of the physics object.
- Add the file OgreMotionState.h to your project.
#ifndef OGREMOTIONSTATE_H #define OGREMOTIONSTATE_H #include "LinearMath\btMotionState.h" #include "OGRE\Ogre.h" class OgreMotionState : public btMotionState { public: OgreMotionState(const btTransform &initialpos, Ogre::SceneNode *node) { mVisibleobj = node; mPos1 = initialpos; } virtual ~OgreMotionState() { } void setNode(Ogre::SceneNode *node) { mVisibleobj = node; } virtual void getWorldTransform(btTransform &worldTrans) const { worldTrans = mPos1; } virtual void setWorldTransform(const btTransform &worldTrans) { if (NULL == mVisibleobj) return; btQuaternion rot = worldTrans.getRotation(); mVisibleobj->setOrientation(rot.w(), rot.x(), rot.y(), rot.z()); btVector3 pos = worldTrans.getOrigin(); mVisibleobj->setPosition(pos.x(), pos.y(), pos.z()); } protected: Ogre::SceneNode *mVisibleobj; btTransform mPos1; }; #endif //OGREMOTIONSTATE_H
- Now we are ready to create some rigid Bodies.
- Lets start by setting the ground as a collision plane.
// Create the collision shape, and give it the ground plane normals. btCollisionShape* groundShape = new btStaticPlaneShape(btVector3(plane.normal.x, plane.normal.y, plane.normal.z), 0); // Change the location of the plane to compensate for the smaller Sinbad. groundNode->setPosition(0, -1, 0); // Create the collision transform. btTransform groundTransform; // Set up the collision location and orientation. groundTransform.setIdentity(); groundTransform.setOrigin(btVector3(groundNode->getPosition().x, groundNode->getPosition().y, groundNode->getPosition().z)); btQuaternion initRotation(groundNode->getOrientation().x, groundNode->getOrientation().y, groundNode->getOrientation().z, groundNode->getOrientation().w); groundTransform.setRotation(initRotation); // Give the plane a mass of 0, because our plane will be static, thus will not moce. btScalar mass(0.0f); // Set the ground as a static object. bool isDynamic = false; // This plane isnt going to be moving so i dont care about setting the motion state btDefaultMotionState* myMotionState = new btDefaultMotionState(groundTransform); btRigidBody::btRigidBodyConstructionInfo rbInfo(mass, myMotionState, groundShape); btRigidBody* body = new btRigidBody(rbInfo); //add the body to the dynamics world _physicsEngine->getDynamicsWorld()->addRigidBody(body);
- Now lets add some cubes :), add this function to your create scene function.
int ringCount = 16; int ringheight = 10; for (int i = 0; i < ringheight; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < ringCount; ++j) { Ogre::Entity* cubeEnt = _sceneManager->createEntity("Cube.mesh"); Ogre::SceneNode* cubeNode = _sceneManager->getRootSceneNode()->createChildSceneNode(); cubeNode->setScale(0.006f, 0.004f, 0.006f); Ogre::Radian angle((Ogre::Math::TWO_PI / ringCount)*j + (Ogre::Math::TWO_PI / ringCount)*0.5*(i%2) ); cubeNode->setOrientation(Ogre::Quaternion(-angle, Ogre::Vector3::UNIT_Y)); //cubeNode->setPosition(j*0.62+((i%2)*0.31f), i*0.405-(1-0.2), 0); cubeNode->setPosition(Ogre::Math::Cos(angle) * 1.9, i*0.405 - (1 - 0.2), Ogre::Math::Sin(angle) * 1.9); cubeNode->attachObject(cubeEnt); btRigidBody* temp = _physicsEngine->AddDynamicCubeRigidBoidy(cubeNode, cubeEnt, 1); temp->setFriction(1); } }
- And finally we must update the dynamicWorld and of course make the camera shoot some boxes! For this you will need to pass to the FrameListener a pointer to the sceneManager and the Physics engine.
- You can either do that via the constructor, or use the lazy way, and make them public, and set them like so
_listener→_physicsEngine = _physicsEngine; - Make the following modifications to your frameListener
Make the FrameListener also inherit from OIS::MouseListenerclass MyFrameListener : public Ogre::FrameListener, OIS::MouseListener
And add the three virtual functions of OIS::MouseListener
virtual bool mousePressed(const OIS::MouseEvent &arg, OIS::MouseButtonID id) { mouseMask |= 1 << (int)id; return true; } virtual bool mouseMoved(const OIS::MouseEvent &arg) { return true; } virtual bool mouseReleased(const OIS::MouseEvent &arg, OIS::MouseButtonID id) { return true; }
And in the constructor: replace
_Mouse = static_cast<OIS::Mouse*>(_InputManager->createInputObject(OIS::OISMouse, false));
with this
// 7.3 Initialize the Mouse input listener. try { _Mouse = static_cast<OIS::Mouse*>(_InputManager->createInputObject(OIS::OISMouse, true)); _Mouse->setEventCallback(this); std::cout << "Successfuly created Mouse"; } catch (...) { std::cout << "Failed to initialize Mouse"; _Mouse = 0; }
Also make sure to add the int member variable mouseMask, and set it to 0 in the FrameListener constructor. Now you can query weather a mouse button was pressed like so
(mouseMask & (1 « (int)OIS::MouseButtonID::MB_Left))
- Now we spawn a cube from the origin of the camera and give it some linear velocity in the direction of the camera.
if ( (mouseMask & (1 << (int)OIS::MouseButtonID::MB_Left)) ) { // Create a cube entity. Ogre::Entity* cubeEnt = _sceneManager->createEntity("Cube.mesh"); Ogre::SceneNode* cubeNode = _sceneManager->getRootSceneNode()->createChildSceneNode(); cubeNode->setScale(0.005f, 0.005f, 0.005f); // Set the position of the cube to the front of the origin of the camera cubeNode->setPosition(_Cam->getPosition() + _Cam->getDirection()); cubeNode->attachObject(cubeEnt); // Now make the cube a rigid body, give it some linearVelocity and add it to the physics world btRigidBody* boxBody = _physicsEngine->AddDynamicCubeRigidBoidy(cubeNode, cubeEnt, 2); boxBody->setLinearVelocity(btVector3(_Cam->getDirection().x, _Cam->getDirection().y, _Cam->getDirection().z) * 30); } - Finally we update the physics world
// Now update the physics world with the delta time. "Note: normally we would want to have the physics world update a little more independant of the framerate, but this will do for now :)" _physicsEngine->getDynamicsWorld()->stepSimulation(evt.timeSinceLastFrame);
When You Are Finished
Upload your commented source files into Lab9 in MySchool (zip them up if more than one).
